
Introduction
With tightening environmental standards for coal-fired power plants, desulfurization wastewater, as a terminal effluent, has raised significant concerns regarding volume reduction and zero discharge. Such wastewater typically contains high salinity, calcium-magnesium hardness, and heavy metals, making it difficult for conventional treatments to achieve stable compliance. Plum Membrane leverages core technologies such as PEK tubular membranes, two-stage nanofiltration, and HRCC high-recovery concentration to provide a comprehensive zero liquid discharge and resource utilization solution, ensuring long-term, stable operations.
Background & Challenges
Desulfurization wastewater originates mainly from wet flue gas desulfurization and presents the following challenges:
Typical Feed Water Characteristics
Process Flow
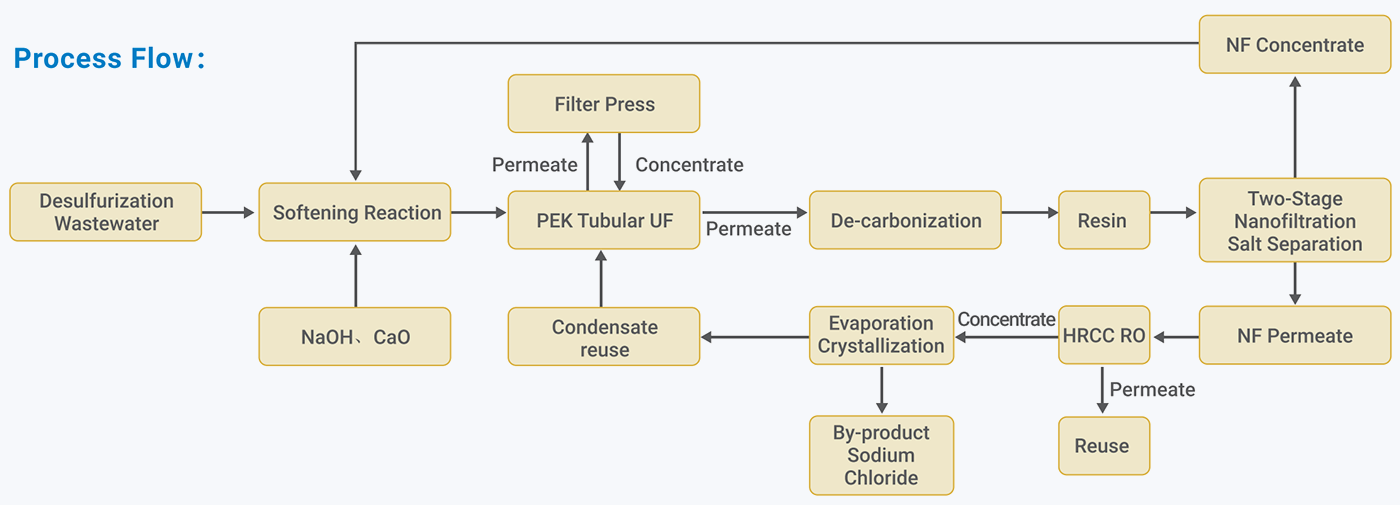
Process Highlight
Ensures product water hardness <50 mg/L, calcium-magnesium <10 mg/L, and silica <20 mg/L, effectively reducing scaling risks.
Sulfate ions are precipitated as calcium sulfate via excess calcium ion reactions, removed by a plate-and-frame filter press system.
NF concentrate maintains a calcium sulfate to sodium chloride ratio >10:1, reducing scaling potential; NF permeate has a sodium chloride to sodium sulfate ratio >60:1, ensuring high purity and stability of crystallized salts.
Highly automated process capable of adapting to water quality fluctuations, ensuring reliability and stable long-term operation.
Applications
Case Photos

Zero Liquid Discharge Process for Power Plant Desulfurization Wastewater

Zero Liquid Discharge Process for Power Plant Desulfurization Wastewater
No. 55 Wuliu Avenue, Xinzhan Hi-Tech Zone, Hefei, Anhui, China






