
Introduction
High-salinity byproducts and fly ash washing wastewater are often generated from industrial wastewater concentration and landfill leachate evaporation systems. These waste streams feature complex salt compositions and high heavy metal content, posing significant treatment challenges. Plum Membrane has developed a comprehensive resource recovery solution utilizing PEK tubular membranes, two-stage nanofiltration, evaporation crystallization, and NF concentrate recycling—shifting the paradigm from end-of-pipe treatment to proactive front-end resource utilization.
Background & Challenges
Typical Feed Water Characteristics
Process Flow
The system is divided into two major paths: "industrial waste salt resource utilization" and "fly ash washing wastewater treatment":
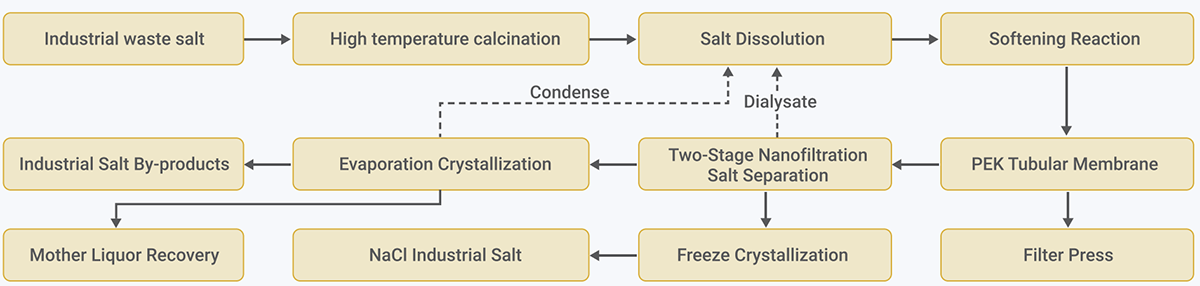
① Resource Recovery from Industrial Waste Salt
Industrial waste salt first undergoes thermosensitive oxidation to remove organic impurities and enhance salt dissolution efficiency. The salt is then dissolved to form a treatable brine solution. This brine is subjected to softening and then processed by a high-flux, fouling-resistant PEK tubular membrane system for solid-liquid separation. Calcium and magnesium are removed to ensure stable and efficient downstream operations. The membrane permeate is further purified and can be reused in the salt dissolution step. The concentrate is directed into a two-stage nanofiltration system for precise separation of sulfate, chloride, and other mixed salts. The resulting high-concentration salt solution enters freezing crystallization and evaporative crystallization systems to produce high-purity industrial salt and sodium sulfate. Crystallization byproducts are centrifuged, packaged, and transported off-site for utilization or disposal. The mother liquor generated during processing can also be reused in the salt dissolution or other parts of the system, minimizing liquid discharge and maximizing salt recovery and resource utilization—transforming waste salt into valuable resources.
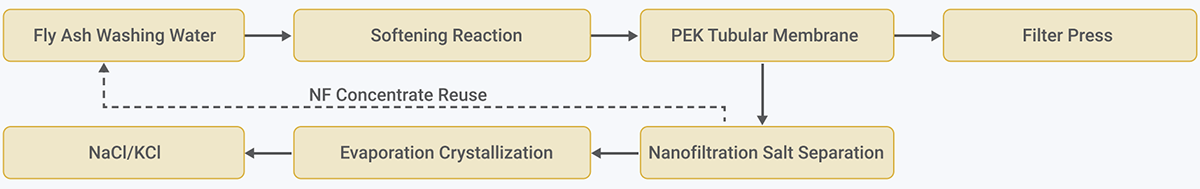
② Fly Ash Washing Wastewater Treatment
Fly ash washing wastewater first enters the softening unit, where alkaline agents such as NaOH or lime are added to remove calcium and magnesium ions and to promote the precipitation of certain heavy metals and suspended solids. After softening, the wastewater flows into the PEK tubular membrane system for cross-flow filtration, effectively removing residual suspended matter and colloids, ensuring high-flux and stable operation. The concentrate from the membrane system enters the sludge removal unit. The extracted sludge is transported off-site, while the filtrate is returned to the front section of the process to improve water recovery. The membrane permeate enters a nanofiltration system for effective salt separation. The resulting NF concentrate is fed into an evaporation and crystallization unit, where reusable industrial salts such as NaCl and KCl are recovered, achieving resource utilization.
Process Highlight
Combining softening and PEK membrane systems, the process effectively removes Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, and heavy metal ions, protecting downstream nanofiltration and crystallization units.
Utilizing two-stage nanofiltration, the system efficiently separates monovalent and multivalent salts; Cl⁻/SO₄²⁻ ratio in NF permeate > 60:1 ensures high crystallized product purity.
Pure salts are extracted via crystallization; remaining mother liquor is recycled or further treated to prevent impurity accumulation and discharge.
The entire system is modular for easy integration and deployment, with automation and monitoring features that reduce manual intervention costs.
Applications
Case Photos

Resource Recovery Process for Waste Salt and Fly Ash Washing Wastewater

Resource Recovery Process for Waste Salt and Fly Ash Washing Wastewater
No. 55 Wuliu Avenue, Xinzhan Hi-Tech Zone, Hefei, Anhui, China






